
Artificial Intelligence (AI) isn’t a novelty, but its rapid emergence in current discussions has made it a highly trending subject. Once associated with futuristic robots, AI has now become an everyday reality, embodied in applications like ChatGPT, Google Bard and Character.ai, thereby democratizing its usage.
The Trend of Global 'AI' Searches Over the Last 5 Years According to Google Trends 1
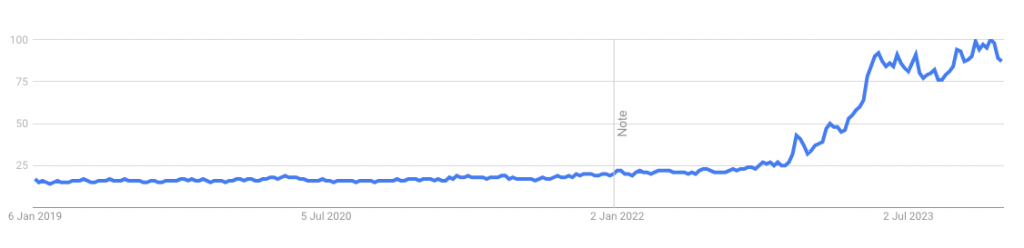
At the heart of this technological revolution, AI no longer remains confined to futuristic visions. It now finds practical applications, especially in customer relations, sparking reflections and inspiring innovative uses. In this specific sector, AI is awakening thoughts and sparking innovative uses.
Understanding AI: An Overview
AI encompasses various facets, from machine learning to deep learning, employing sophisticated algorithms to simulate human cognitive processes. It is an evolving and adaptable technology that powers various diverse applications.
AI Definition:
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to a computer system’s ability to perform tasks that would normally require human intelligence. This includes problem-solving, learning, natural language understanding, pattern recognition, and much more.
Types of AI:
Narrow AI (or Weak AI): Specialized in a specific task. For instance, an algorithm playing chess or categorizing images.
Strong AI (or General AI): Can adapt to different tasks and solve problems in a manner similar to a human being.
AI Techniques:
Machine Learning : An AI approach where systems learn from data without being explicitly programmed. For example, recommendation algorithms used by Netflix.
Deep Learning : A subset of machine learning using deep neural networks to learn from data. For instance, neural networks used for image recognition.
The difference between these two techniques lies in their approach: machine learning employs algorithms to identify patterns in data and make decisions based on these patterns. In contrast, deep learning, a subset of machine learning, uses deep neural networks to learn hierarchical representations of data. For example, generative AI* applications like ChatGPT belong to the field of Deep Learning.
* Generative AI is a specific branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on creating content, text, images, music, etc., autonomously, similar to the way a human being would.
AI Serving Customer Experience
In today’s commercial landscape, delivering an exceptional customer experience is imperative for any business looking to stand out. Artificial intelligence (AI) emerges as a pivotal tool to optimize this experience, offering innovative and personalized solutions. By leveraging advancements in deep learning and natural language processing, AI transforms online interactions, providing instant responses, enhanced personalization, and anticipatory services, thereby redefining the benchmarks of modern customer experience.
1. Instant Responses and Continuous Assistance:
AI-powered virtual agents like chatbots and voicebots enable immediate responses to customer queries, offering 24/7 support. These systems can analyze questions, contextually respond, and guide users to suitable solutions. For instance, a chatbot can assist a customer in navigating a website to find a specific product or provide information about company services.
Advantage of AI: contextual understanding, learning capacity, more sophisticated responses.
2. Advanced Personalization:
AI analyzes customer data to create personalized experiences. Using predictive algorithms, it tailors recommendations and offerings based on individual preferences. For instance, for the telesales team, employing AI enables product suggestions based on purchase history, demographic, and behavioral data specific to each user.
Advantage of AI: massive data processing, dynamic adaptation, proactive responses.
3. Vocal Analysis for Enhanced Engagement:
AI understands and analyzes emotions and intentions through voice. It evaluates tones, keywords, and intonations to adapt responses and interactions. For instance, within call centers, voice analysis tools can assess customer satisfaction during phone conversations, facilitating appropriate responses to better meet customer needs and expectations.
Advantages of AI: emotion analysis, detection of unexpressed needs, rapid responses.
4. Agent Training and Assistance:
AI provides real-time information to human agents during customer interactions. It can suggest responses, provide relevant data, and help in faster problem resolution. For example, AI can offer pre-approved responses to guide customer service agents.
Advantages of AI: immediate assistance, individual adaptation, trend tracking.
5. Call Center Planning and Management:
AI optimizes call center management and planning by utilizing predictive analysis. It uses historical data to anticipate call spikes and optimize staffing, ensuring better responsiveness.
Advantages of AI: forecast accuracy, adaptability.
6. Process Automation:
Repetitive tasks such as data collection, issue tracking, and case management can be automated using AI, freeing up agent time for more complex and human-focused interactions. For example, AI systems can automatically classify customer queries and assign them to specialized agents.
Advantages of AI: scalability, continuous improvement.
AI: A Complement, Not a Replacement
However, despite its advancements, AI cannot replace contact center agents. Human skills such as empathy, creativity, and complex problem-solving remain irreplaceable. The balance lies in the combined use of AI and human agents, maximizing operational efficiency while preserving a quality customer experience.
Ultimately, AI revolutionizes both customer experience and contact center operations. Yet, its full potential will only be realized by working in synergy with human capabilities, creating a superior and more efficient customer experience.
Ino Global offers an omnichannel contact center solution with AI capabilities. Our aim is to help you integrate AI into your customer experience center.

Vous avez des projets ? Contactez-nous !
CREATING EXCEPTIONAL CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP
Receive our latest news directly in your inbox.
|
|
Thank you for Signing Up |


Creating exceptional customer relationship
Receive our latest news directly in your inbox.
| Thank you for Signing Up |


